Advertisements
Blood glucose control is essential for health, as adequate sugar levels provide the energy needed for the body to function properly.
Keeping these levels balanced is essential to prevent complications, especially in people with diabetes or prediabetes. In this article, we'll explore what glucose is, why it's important to keep it under control, and what strategies you can implement to achieve this.
Advertisements
What is Glucose and Why is it Important to Control It?
Glucose is a simple sugar obtained primarily from the carbohydrates we consume. It is the main source of energy for our body's cells.
See also
Advertisements
- Advantages of 5G: Unlimited Connection
- Learn to Play Guitar: Practical Guide
- Optimize your device's storage
- Night Vision on Cell Phones
- Protect your cell phone: the importance of an antivirus
Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps glucose enter cells, where it is used for energy.
Maintaining stable glucose levels is vital because:
- Constant Energy:
The brain, muscles, and other organs depend on glucose to function optimally. - Prevention of Complications:
Hyperglycemia (high glucose levels) can damage blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of heart problems, kidney damage, and eye complications. On the other hand, hypoglycemia (low levels) can cause dizziness, confusion, and, in extreme cases, loss of consciousness. - Metabolic Control:
Good glucose management helps prevent long-term complications, improving quality of life, especially in people with diabetes.
Factors that Influence Glucose Levels
Several factors can affect blood glucose levels. Understanding them is the first step to managing them effectively:
- Feeding:
The types and amounts of carbohydrates consumed directly influence glucose levels. High-glycemic foods can cause rapid spikes, while low-glycemic foods help maintain more stable levels. - Physical Activity:
Exercise improves insulin sensitivity and helps cells use glucose more effectively, which promotes glucose stability. - Stress:
Stress can trigger the release of hormones that raise blood glucose levels, making it difficult to control, especially in people with diabetes. - Sleep Quality:
Lack of sleep or poor quality sleep can disrupt hormonal regulation and increase insulin resistance. - Medication:
In people with diabetes, medication use and adherence are critical to maintaining glucose balance.
Strategies for Glucose Control
To achieve good glucose control, it's important to integrate various strategies into your daily routine. Here are some of the most effective:
1. Healthy Eating
A balanced diet is the cornerstone of glycemic control:
- Complex Carbohydrates:
Choose whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, which release energy gradually and prevent glucose spikes. - Low Glycemic Index:
Prioritize low-glycemic foods, such as oats, quinoa, and sweet potatoes, to maintain stable levels. - Fibers and Proteins:
Fiber slows the absorption of sugar, and protein helps maintain satiety. Include fruits, vegetables, and lean sources of protein at every meal. - Controlled Portions and Regular Schedules:
Spreading meals into several small portions throughout the day helps avoid large fluctuations in glucose.
2. Constant Physical Activity
Regular exercise is crucial to improving insulin sensitivity:
- Aerobic Exercises:
Activities such as walking, running, swimming, or cycling are ideal for lowering blood glucose levels. - Strength Training:
Incorporating resistance exercises helps increase muscle mass, which improves glucose utilization. - Daily Routine:
Even everyday activities can make a difference. Try to integrate movement into your daily routine and establish an exercise routine of at least 30 minutes a day.
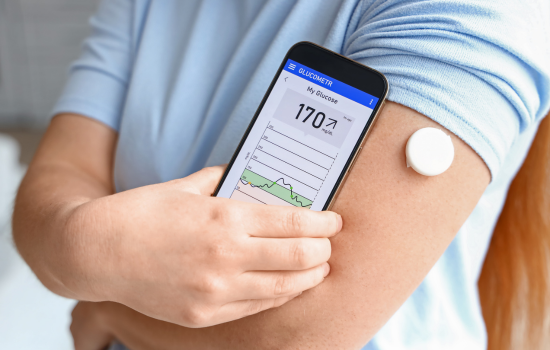
3. Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Keeping a constant record of your glucose levels allows you to adjust your habits and treatment:
- Use of Glycosimeters:
Perform regular tests at different times of the day to identify patterns and adjust diet or medication as needed. - Continuous Monitoring (CGM):
Continuous monitoring systems allow glucose to be measured in real time, providing early warnings of sudden changes. - Mobile Applications:
There are apps that sync with measuring devices to record and analyze your levels, making it easier to communicate with your doctor.
4. Appropriate Use of Medication and Medical Follow-up
Medication is essential for people with diabetes, but its effectiveness depends on correct use:
- Adherence to the Prescription:
Take your medication exactly as prescribed by your doctor, without skipping doses. Use reminders or apps to manage your schedule. - Regular Consultations:
Regular visits to the endocrinologist are essential to adjust treatment and prevent complications. - Continuing Education:
Educate yourself about your condition and participate in support groups to stay up-to-date on best practices for managing diabetes.
5. Stress Management and Sleep Quality
Emotional well-being and good rest are key to effective glucose control:
- Relaxation Techniques:
Practice meditation, yoga, or breathing exercises to reduce stress, which can help stabilize blood sugar levels. - Sleep Hygiene:
Establish a bedtime routine, create a conducive environment (dark, quiet, and cool), and avoid using electronic devices before bed. - Recreational Activities:
Make time for hobbies and activities that relax you. A good balance between work and rest is vital for glucose control.
Tools and Support Technologies
Technology can be a great ally in glucose management. Some useful tools include:
- Monitoring Applications:
Apps that record your glucose readings and generate graphs to identify patterns, making it easier to adjust your treatment. - Continuous Monitoring Devices:
Sensors that measure glucose in real time and send alerts to your phone, allowing you to intervene immediately. - Digital Diaries:
Tools that allow you to record your diet, exercise, and other factors, helping you correlate your glucose levels with your daily habits.
These technologies not only make glucose control easier, but also empower you to make more informed decisions and improve your overall health.
Conclusion
Glucose control is essential for maintaining health and preventing long-term complications, especially in people with diabetes or prediabetes. Adopting a comprehensive approach that combines a balanced diet, regular exercise, consistent monitoring, appropriate medication use, and stress and sleep management is key to achieving stable glucose levels.
By integrating these strategies into your daily routine and leveraging technological tools, you can transform glucose management into an effective and proactive part of your lifestyle. Remember that consistency, ongoing education, and collaboration with healthcare professionals are essential to achieving and maintaining balance.
Start implementing these strategies today and enjoy a healthier life, with stable glucose levels and overall well-being! With commitment and the right tools, glucose control will become an ally on your path to a better quality of life.
Access the stores to download the applications here






